Measurement methods
Dissipation factor and partial discharge measurement

Whether dissipation factor or partial discharge measurement – both diagnostics methods have their advantages. However, individually, neither of them can detect all weak points. For this reason, it is worthwhile combining both procedures – whether carried out subsequently or together in one procedure.
truesinus®

Compact and powerful – BAUR truesinus® voltage sources
The BAUR truesinus® voltage sources are handy and suitable for all relevant daily tasks – whether cable testing or diagnostics. They ensure highly reliable results and, thanks to the truesinus® technology developed by BAUR, they provide an ideally formed low-frequency sine voltage as well as the DC voltage required for sheath testing.
With truesinus®, BAUR offers state-of-the-art technology for generating voltage with VLF (Very Low Frequency 0.1 Hz) and thus enables the least destructive testing and diagnostics of modern medium-voltage cables in compliance with the standards.
The BAUR portfolio covers all the important requirements of network operators with regard to testing and diagnostics technology in the medium-voltage range. Our well-thought-out and cleverly devised test and diagnostics systems enable fully automatic VLF cable testing, meaningful dissipation factor measurement (tan delta), and high-precision partial discharge measurement. Intelligent software features also allow sequences to be performed in parallel, saving considerable time and costs.
Highly accurate tan δ measurement
Thanks to the ideally formed truesinus®, you can rely on highly accurate measurements of the tan δ (tan delta or TD) and meaningful results for partial discharge measurement, as well as good reproducibility and comparability of the measured values.
What you stand to gain with truesinus® technology
The VLF 0.1 Hz sine voltage is much more suitable for the tan δ measurement, which is important for condition evaluation, than other typical voltage shapes or frequencies. The ideal, long-waved sine makes it possible to acquire TD measurement results with the highest resolution. With these results, small rises and detailed properties can be recognised and evaluated. With regard to the dissipation factor measurement, the measurement with truesinus® is more sensitive than a measurement with operating frequency.
Advantages
- Load-independent measurement results
- Highly accurate tan delta
- Reproducible, precise measurements
- Possible to carry out testing and diagnostic measurements in parallel (Monitored Withstand Test)
- Short measuring time
- Compact voltage sources
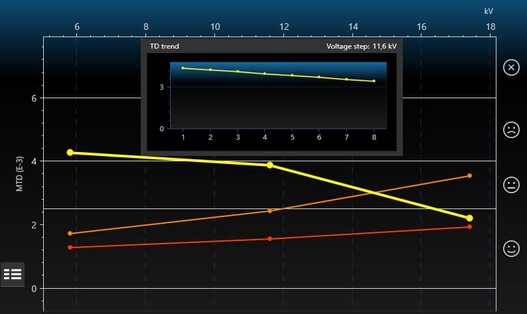
Dissipation factor measurement (tan δ measurement)
The dissipation factor measurement (tan δ measurement) is a non-destructive and integral procedure that serves to evaluate the condition of an entire cable route. With the dielectric dissipation factor tan δ, the relation of effective power to reactive power of the cable is measured. The measurement provides clear information on the condition of the cable insulation and its ageing.
With the dissipation factor measurement, you can detect
- water-damaged spots (water trees) in the insulation of XLPE cables, which later lead to electrical trees and represent the natural cause of a cable fault.
- Faults in the insulation of paper-insulated mass-impregnated cables due to drying
- Insufficient insulation of paper-insulated mass-impregnated cables due to moisture
- Possible partial discharges
- Possible ageing effects in cable routes
Partial discharge testing
Partial discharges occur at faults in the cable, e.g. at electrical trees, joints and terminations. Partial discharge diagnostics is used to determine possible fault locations in cables and accessories before they lead to failure. This makes it possible to rectify the problem in a timely manner and prevent any subsequent damage resulting from uncontrolled failures. Partial discharge measurement is conducted in accordance with standard IEC 60270.
Detect the following with partial discharge measurement
- Faults in new and old cable accessories, such as incorrectly fitted joints
- Faults in the insulation of XLPE cables (e.g. electrical trees)
- Insufficient mass-impregnated paper insulation due to drying
- Mechanical damage to the cable sheath
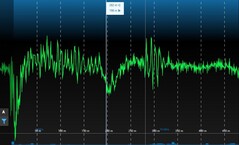
PD signal superimposed with faults
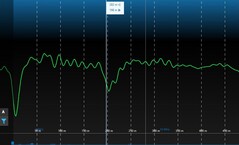
Signal cleaned with filter
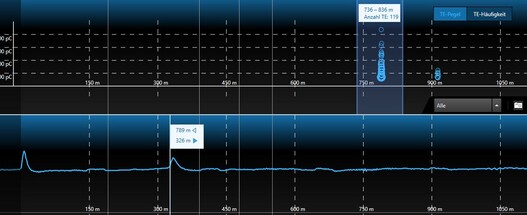
Combined presentation of location and PD assessment
BAUR PD measuring devices can diagnose the following:
- PD localisation
- PD level
- PD inception voltage / extinction voltage
- PD quantity
Supporting functions
- Phase-resolved PD presentation for every
- Fault
- PD interference filter function
- Joint localisation
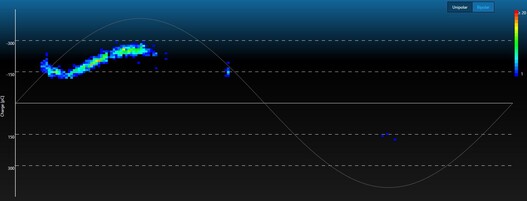
Phase resolving for a PD position
Phase-resolved PD presentation (PRPD)
The phasing of partial discharges can be determined through state-of-the-art analysis methods. This makes it possible for you to assign the fault to diverse types of fault and to plan subsequent measurements as well as repair measures in a target-oriented and time- and cost-saving manner.
Online PD testing

With the help of liona, the portable BAUR online PD spot tester, cables can also be quickly and easily tested for partial discharges whilst live (online). The DeCIFer algorithm supports the detection of partial discharge signals from noise signals. The online PD test helps to detect approximate weak points without switching off the system and, if required, to localise faults.
liona and iPD – a unique solution
- For PD testing during normal mains operation if cables cannot be taken out of operation
- For inexpensive testing of HV cable routes – even in the case of cross bonding
- For straightforward initial estimation of PD
- For temporary monitoring of a cable route
Advantages
- Automatic PD detection – even at high noise levels
- PD spot test in 3 minutes – connect, > measure > read result
- Unique technology for online PD mapping using artificial reflection
- Easy-to-install, temporary monitoring system
- Simple testing of MV and HV cables
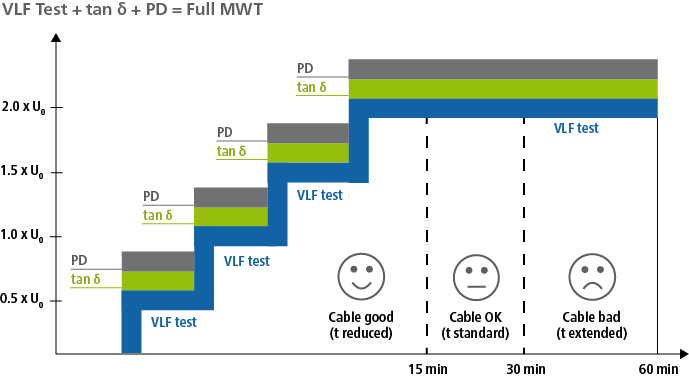
Monitored Withstand Test
The time-saving combination of testing and diagnostics is known as the Monitored Withstand Test (MWT). The MWT provides significant information for the condition evaluation and allows for the required test duration to be adapted to the cable condition. The combined procedure is recognised by the IEEE and IEC, and is recommended as an appropriate measurement method for service-aged cable systems.
Phase 1
The procedure programmed in the BAUR devices for the MWT is split into two stages: The diagnostic measurement takes place in the voltage build-up stage so that you can get an idea of the cable condition; significantly aged cables are detected and you can take prompt action to ensure that pre-damaged cables are not exposed to the test voltage unnecessarily.
Phase 2
During the MWT stage, in which the diagnostics are carried out in parallel to the cable testing, you can detect the time response of tan δ. During the Full Monitored Withstand Test, the partial discharge measurement is also executed and PD faults can be simultaneously indicated and precisely localised.
Condition-based test duration
The condition-based test duration offers a big advantage to you as the operator. Based on positive diagnostics values, cable testing can be shortened to 15 minutes so that the cable is not under load for an unnecessarily long period of time.
Full Monitored Withstand Test
Carrying the cable testing and cable diagnostics out in parallel (with tan-δ measurement or partial discharge measurement) in the Monitored Withstand Test saves time and provides valuable information for asset management.
Detailed information on cable testing and diagnostic



